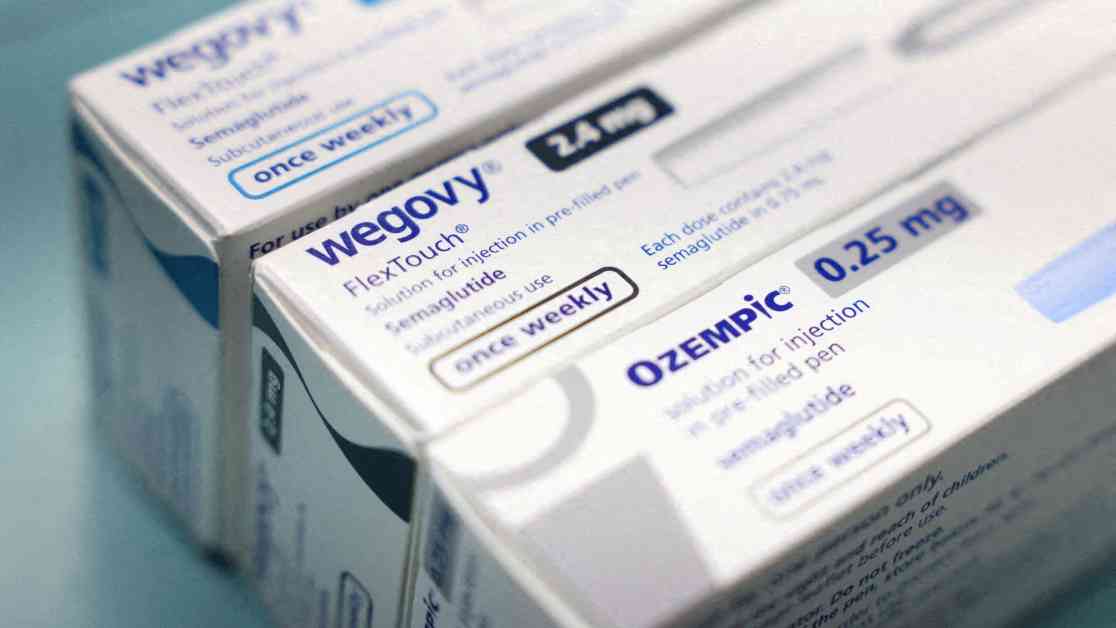
The FDA has finally resolved the shortage of Wegovy and Ozempic drugs, two popular medications manufactured by Novo Nordisk, after more than two years of supply constraints. This news comes as a relief to patients across the country who have been struggling to access these crucial injections for weight loss and diabetes treatment. The shortage of these drugs had led many patients to turn to compounding pharmacies for unapproved versions of Wegovy and Ozempic, which were far cheaper but not FDA-approved. With the FDA’s recent decision, compounding pharmacies will no longer be able to produce these unbranded versions of the medications, signaling a significant shift in the pharmaceutical landscape.
Novo Nordisk’s stock saw a 5% increase following the FDA’s announcement, while Hims & Hers, a telehealth company offering compounded Wegovy and Ozempic, experienced a sharp decline in shares. The shortage of the active ingredient in both drugs, semaglutide, had been a major contributing factor to the prolonged scarcity of Wegovy and Ozempic in the U.S. market. The demand for these drugs had soared since 2022, leading Novo Nordisk and its competitors to invest heavily in expanding their manufacturing capacities.
The FDA’s evaluation determined that Novo Nordisk now has the supply and manufacturing capabilities to meet the current and future demand for semaglutide injections in the U.S. However, the agency also cautioned that there may still be intermittent and localized supply disruptions as the products make their way through the distribution chain to pharmacies. This news is a significant win for Novo Nordisk and positions them well to compete with Eli Lilly, their rival in the weight loss drug market, which analysts predict could be worth more than $150 billion annually after 2030.
Implications for Compounded Medications
The FDA’s decision marks the end of an era where compounding pharmacies could produce unapproved versions of semaglutide without facing repercussions. The agency has given these pharmacies a transition period of 60 to 90 days to cease the production of compounded semaglutide, allowing patients time to switch to the branded versions of the medications. While this may pose a challenge for patients who relied on compounded versions due to cost reasons, the FDA’s move underscores the importance of ensuring patient safety and access to FDA-approved medications.
Some patients turned to compounded versions of Wegovy and Ozempic because they lacked insurance coverage for Novo Nordisk’s drugs, which can cost around $1,000 a month. While Ozempic is typically covered by most health plans, medications like Wegovy are not currently covered by Medicare and other insurance providers. This gap in coverage highlights the broader issue of access to affordable medications for patients with chronic conditions like obesity and diabetes.
Expert Insights and Market Trends
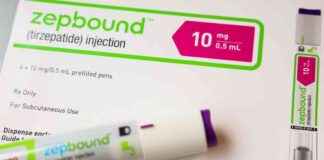
The shortage of tirzepatide, the active ingredient in Eli Lilly’s Zepbound and Mounjaro injections, was recently resolved by the FDA, setting the stage for increased competition between Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly in the weight loss drug market. Analysts predict significant growth in this market, with estimates exceeding $150 billion annually post-2030. The FDA’s decision to address the shortage of Wegovy and Ozempic could have far-reaching implications for the pharmaceutical industry and patients seeking innovative treatments for weight management and diabetes.
In conclusion, the resolution of the Wegovy and Ozempic shortage by the FDA marks a significant milestone in the pharmaceutical landscape. Patients, healthcare providers, and industry stakeholders alike are closely watching the developments in the weight loss drug market as companies like Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly vie for dominance. The impact of these decisions on patient access, affordability, and treatment outcomes underscores the critical role of regulatory agencies in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medications for those in need. The journey towards resolving drug shortages and improving patient care continues, with each milestone shaping the future of healthcare in the U.S.